Ingredient spotlight

• The difference between pre/pro/post biotics
• Impacts of gut health and exercise
• The science of Immuse™ and immune support
watch the interview
Join Kyowa’s VP of Scientific Affairs, Danielle Citrolo, and Move Nutrition editor Elyse Lovett as they discuss the microbiome, the emergence of postbiotics, and how gut health impacts exercise.
Sponsored Content
A Healthy Gut
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) is home to trillions of microorganisms, bacteria, and fungi, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microbes play a crucial role in various aspects of health including digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and mental health. There are many factors that contribute to a healthy gut including the following:
A Balanced Diet
Consuming a wide range of whole foods including fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Pre, Pro, and Postbiotics
Beneficial bacteria can be consumed through certain fermented foods and non-digestible fibers as well as through supplementation. These beneficial bacteria can help restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, but can also have beneficial effects outside of the gastrointestinal track
Physical Activity
Regular exercise promotes health digestion and -is recommended for overall good health and wellbeing.
The gut microbiome helps maintain a healthy GI tract by promoting proper digestion and nutrient absorption. The microbes break down complex carbohydrates and fiber that the body cannot digest producing short-chain fatty acids that nourish the cells in the gut. Over 80% of your immune cells are located in the gut, so what you consume on a daily basis can have a tremendous impact on how you feel and move every day. This is the link to your gut – immune health connection and the importance biotics can have within your body.
Prebiotics and Probiotics vs. Postbiotics
In short, prebiotics and probiotics directly introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut. Prebiotics are types of dietary fibers that are indigestible by the body but serve as a food source to stimulate the growth and activity of specific beneficial bacteria in the gut. Prebiotics also act as fuel for beneficial microbes helping them maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Probiotics are living microorganisms which are mainly bacteria and some yeasts found in fermented foods like yogurt and sauerkraut. Probiotics help restore and maintain a healthy balance of the gut microbiota and can support digestion, nutrient absorption, and many other functions including immune.
Postbiotics defined by ISAPP’s consensus paper are a preparation of inanimate microorganisms and/or their components that confers a health benefit on the host. Postbiotics can offer a different approach than prebiotics by supporting the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria already present in the gut without the need for live microorganisms.
Postbiotics are a preparation of inanimate microorganisms that confer a health benefit on the host
Unlike probiotics, postbiotics are not living microorganisms, but rather nonviable microbial cells that provide health-promoting properties when consumed. Referred to as the probiotic paradox, scientists have long known that many of the beneficial effects obtained from live cells can also be obtained by consuming a population of dead cells. Postbiotics are becoming more in demand by consumers and production methodologies are being explored by ongoing research to produce postbiotics in a controlled and efficient way.
Award Winning Immuse™

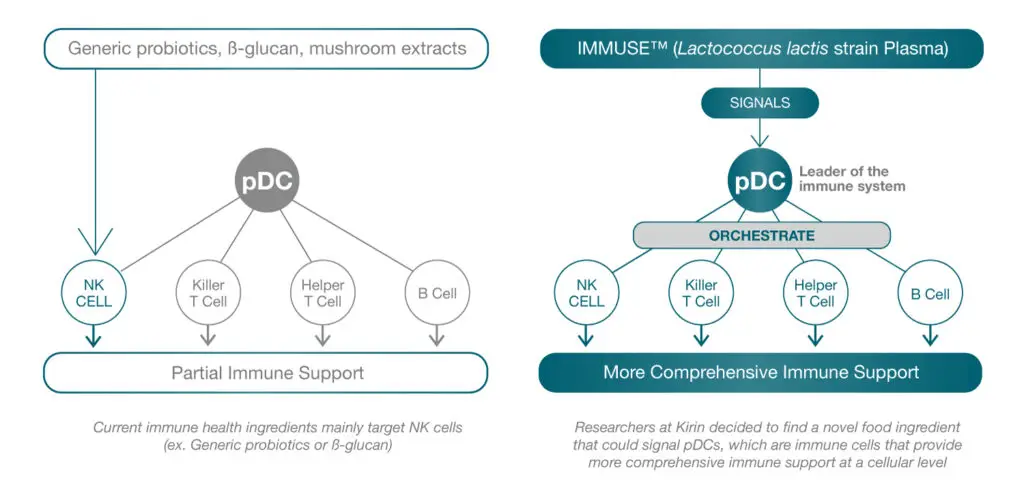
IMMUSE™ is a novel postbiotic strain – Lactococcus Lactis strain Plasma (LC-Plasma). Supported by over 30 clinical studies, IMMUSE has been studied to promote immune health*; signal the body’s natural defenses at the cellular level*; and help maintain physical condition for year-round support*. The postbiotic is the first lactic acid bacteria that has been clinically researched to directly signal plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), a rare subset of immune cells, to provide more comprehensive immune support*.
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are specialized immune cells involved in the body’s immune response primarily found in peripheral lymphoid tissues such as lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen. These specialized immune cells are a subset of dendritic cells which are key players in the immune system and act to detect pathogens by signaling immune responses. PDCs are known as the ‘commander-in-chief’ of bridging the gap between ingredients that offer basic and advanced systems of immune system response.
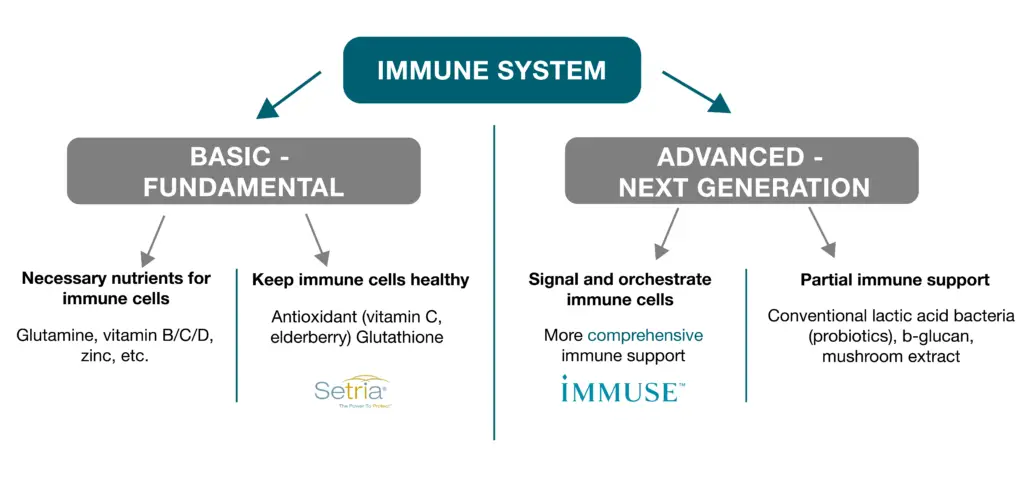
Most immune-activating ingredients on the market such as conventional probiotics offer basic or fundamental functionality providing partial immune support by signaling only one type of immune cell, mainly natural killer (NK) cells. IMMUSE provides advanced functionality offering a more comprehensive approach by orchestrating a wide variety of immune type cells including NK cells, killer T-cells, helper T-cells, and B-cells.
An Advanced Immune Ingredient Built on Kyowa Hakko Kirin’s Deep-Rooted Science
Advances in Science Since 1949
Kyowa Hakko Bio Co., Ltd., and Kirin Holdings Company have a business relationship that involves collaborations in the field of fermented-based products. Kirin Holdings is a major Japanese beverage company with a diverse portfolio of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages and pharmaceuticals. The collaboration between the two companies began in 2008 when Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd (KHK) was established.
Kyowa Hakko’s rich history in the development and production of fermentation-based products has made the company a leader in ingredient innovation technology and science-based product development. The company leverages its 60+ years of knowledge in fermentation technology to develop and produce various products including amino acids and clinically researched ingredients used in a wide variety of applications. Kyowa’s advanced expertise in fermentation processes allows for the creation of high-quality and innovative solutions. Kyowa Hakko’s and Kirin Holdings’ commitments to quality, innovation, and scientific research have earned them a reputation as a trusted and reliable supplier and manufacturer of innovative products in the fields of health, nutrition, and pharmaceuticals.
60+ years of knowledge in fermentation technology
During Kyowa Hakko’s early years of development, the company was the first in the world to invent the process of L-glutamic acid production by fermentation. The company then expanded its fermentation capabilities and began producing a broader range of amino acids through advanced technology. The development of amino acids such as glutamine, arginine, and citrulline made Kyowa Hakko a world leader in the development of amino acids using high-yield fermentation processes.
KHK on the Forefront of Immune Health
Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co. is proud to bring one of its best-selling immune health products, IMMUSE™, in Japan to the United States as an immune health ingredient. The products popularity and credibility in Japan is interesting as it is the first ingredient with a Functional Claim for immunity in Japan. In addition, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co. has won many local and global awards for the outstanding science behind its ingredient.
sponsored content from


Subscribe for additional Move Nutrition Quarterly content like research updates, market insights, and more.


